Page 342 - Emerging Trends and Innovations in Web-Based Applications and Technologies
P. 342
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) @ www.ijtsrd.com eISSN: 2456-6470
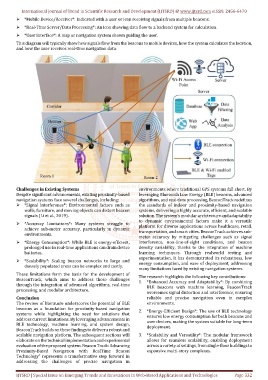
Ø *Mobile Device/Receiver*: Indicated with a user or icon receiving signals from multiple beacons.
Ø *Real-Time Server/Data Processing*: An icon showing data flow to a backend system for calculation.
Ø *User Interface*: A map or navigation system shown guiding the user.
This diagram will typically show how signals flow from the beacons to mobile devices, how the system calculates the location,
and how the user receives real-time navigation data.
Challenges in Existing Systems environments where traditional GPS systems fall short. By
Despite significant advancements, existing proximity-based leveraging Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons, advanced
navigation systems face several challenges, including: algorithms, and real-time processing, BeaconTrack redefines
Ø *Signal Interference*: Environmental factors such as the standards of indoor and proximity-based navigation
walls, furniture, and moving objects can distort beacon systems, delivering a highly accurate, efficient, and scalable
signals (Li et al., 2019). solution. The system’s modular architecture and adaptability
to dynamic environmental factors make it a versatile
Ø *Accuracy Limitations*: Many systems struggle to platform for diverse applications across healthcare, retail,
achieve sub-meter accuracy, particularly in dynamic transportation, and smart cities. BeaconTrack achieves sub-
environments.
meter accuracy by mitigating challenges such as signal
Ø *Energy Consumption*: While BLE is energy-efficient, interference, non-line-of-sight conditions, and beacon
prolonged use in real-time applications can drain device density variability, thanks to the integration of machine
batteries. learning techniques. Through realworld testing and
experimentation, it has demonstrated its robustness, low
Ø *Scalability*: Scaling beacon networks to large and energy consumption, and ease of deployment, addressing
densely populated areas can be complex and costly.
many limitations faced by existing navigation systems.
These limitations form the basis for the development of The research highlights the following key contributions:
BeaconTrack, which aims to address these challenges 1. *Enhanced Accuracy and Adaptability*: By combining
through the integration of advanced algorithms, real-time BLE beacons with machine learning, BeaconTrack
processing, and modular architecture.
overcomes signal distortion and interference, ensuring
Conclusion reliable and precise navigation even in complex
The review of literature underscores the potential of BLE environments.
beacons as a foundation for proximity-based navigation 2. *Energy-Efficient Design*: The use of BLE technology
systems while highlighting the need for solutions that ensures low energy consumption for both beacons and
address current limitations. By leveraging advancements in user devices, making the system suitable for long-term
BLE technology, machine learning, and system design, deployment.
BeaconTrack builds on these findings to deliver a robust and
scalable navigation platform. The subsequent sections will 3. *Scalability and Versatility*: The modular framework
elaborate on the technical implementation and experimental allows for seamless scalability, enabling deployment
evaluation of the proposed system. Beacon Track: Advancing across a variety of settings, from single-floor buildings to
Proximity-Based Navigation with RealTime Beacon expansive multi-story complexes.
Technology" represents a transformative step forward in
addressing the challenges of precise navigation in
IJTSRD | Special Issue on Emerging Trends and Innovations in Web-Based Applications and Technologies Page 332