Page 562 - Emerging Trends and Innovations in Web-Based Applications and Technologies
P. 562
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) @ www.ijtsrd.com eISSN: 2456-6470
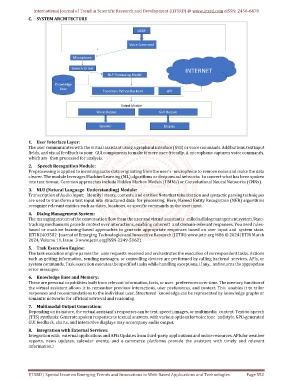
C. SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
1. User Interface Layer:
The user communicates with the virtual assistant using a graphical interface (GUI) or voice commands. Add buttons, text input
fields, and visual feedback to your GUI components to make it more user-friendly. A microphone captures voice commands,
which are then processed for analysis.
2. Speech Recognition Module:
Preprocessing is applied to incoming audio data originating from the user's microphone to remove noise and make the data
clearer. The module leverages Machine Learning (ML) algorithms or deep neural networks to convert what has been spoken
into text format. Common approaches include Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) or Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs).
3. NLU (Natural Language Understanding) Module:
Transcription of Audio Input: Identify intents, contexts, and entities Note that tokenization and syntactic parsing techniques
are used to transform a text input into structured data for processing. Here, Named Entity Recognition (NER) algorithms
recognize relevant entities such as dates, locations, or specific commands in the user input.
4. Dialog Management System:
The managing system of the conversation flow from the user and virtual assistant is called a dialog management system. State-
tracking mechanisms provide context over interactions, enabling coherent and domain-relevant responses. You need rules-
based or machine learning-based approaches to generate appropriate responses based on user input and system state.
JETIR2403582 Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research (JETIR) www.jetir.org f686 © 2024 JETIR March
2024, Volume 11, Issue 3 www.jetir.org(ISSN-2349-5162)
5. Task Execution Engine:
The task execution engine parses the user requests received and orchestrates the execution of correspondent tasks. Actions
such as getting information, sending messages, or controlling devices are performed by calling backend services, APIs, or
system commands. Task execution executes the specified tasks while handling exceptions, if any, and returns the appropriate
error messages.
6. Knowledge Base and Memory:
These are personal capabilities built from relevant information, facts, or user preferences over time. The memory function of
the virtual assistant allows it to remember previous interactions, user preferences, and context. This enables it to tailor
responses and recommendations to the individual user. Structured knowledge can be represented by knowledge graphs or
semantic networks for efficient retrieval and reasoning.
7. Multimodal Output Generation:
Depending on its nature, the virtual assistant's responses can be text, speech, images, or multimedia content. Text-to-speech
(TTS) synthesis: Generate spoken responses to textual answers, with various options for voice tone and style. GPU-generated
GUI feedback, charts, and interactive displays may accompany audio output.
8. Integration with External Services:
Integration with external applications and APIs Updates from third-party applications and online resources. APIs for weather
reports, news updates, calendar events, and e-commerce platforms provide the assistant with timely and relevant
information.!
IJTSRD | Special Issue on Emerging Trends and Innovations in Web-Based Applications and Technologies Page 552