Page 408 - Emerging Trends and Innovations in Web-Based Applications and Technologies
P. 408
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD)
Special Issue on Emerging Trends and Innovations in Web-Based Applications and Technologies
Available Online: www.ijtsrd.com e-ISSN: 2456 – 6470
A Meta-Learning Method for Few-Shot
Face Forgery Segmentation and Classification
2
3
1
4
Govind Raut , Prof. Harshita , Chandrakant Kottalwar , Prof. Anupam Chaube
1,2,3,4 Department of Science and Technology,
1,2,3 G H Raisoni Institute of Engineering and Technology, Nagpur, Maharashtra, India
4 G H Raisoni College of Engineering and Management, Nagpur, Maharashtra, India
ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
Detection of Forgeries in Images: A Survey Abstract: While The development of deep learning in recent years has
the technology to detect forgeries in images is able to tremendously improved the problem of falsified facial photos
detect images even at complex images, this well is only as a security threat. Deep learning has also been used for
limited to known forgery methods. It trains neural detection in order to conduct forensic analysis on these kinds
networks from large amounts of original and corresponding of falsified photos. Presently available technology for
forged images created with known techniques. But it fails to identifying forged photos does a good job of identifying
process unseen forgery techniques. One such proposed established forging techniques. This system trains neural
solution to this problem, recently, is to employ a hand- networks, which serve as detectors for learning the features
crafted generator of forged images to generate a series of of forged images, using a huge number of original and related
fake images and feed them to the neural network for forged images produced using known forged techniques.
training However, the aforementioned approach has Nevertheless, when these techniques come against untrained
certain limitations detecting performance in situations forged methods, their detection efficiency significantly
where the hand-craft generator has not taken into declines. Recently, an innovative approach has been put out
consideration invisible forging processes. In this study, we to overcome this problem [1]. Using a parameterizable
use a meta-learning approach to create a highly adaptive forged image generator, this technique generates a variety of
detector for detecting novel forging techniques, overcoming forged images, which are subsequently used to train a neural
the drawbacks of current approaches. By employing meta- network. The forged image generator is trained using the
learning approaches to train a forged image detector, the immaculate image, as shown in Figure 1. Forging technique A
suggested method allows the detector to be fine-tuned and forging method B are two of the mechanisms used by the
using a small number of fresh forged examples. In order to forged image generator/synthesizer G to produce forged
detect forged images with comparable characteristics, the images. The forged picture detector is then trained using
suggested method inputs a limited number of the forged these artificially created forged images. Given that the
images to the detector and allows the detector to modify its generator of faked images was created by
weights based on the statistical properties of the input
forged photos. With IoU gains ranging from 35.4% to
127.2%, the suggested approach significantly improves
forgery method detection. These findings illustrate that the
suggested approach outperforms the state-of-the-art
techniques in the majority of situations and greatly
enhances detection performance with a relatively small
number of samples.
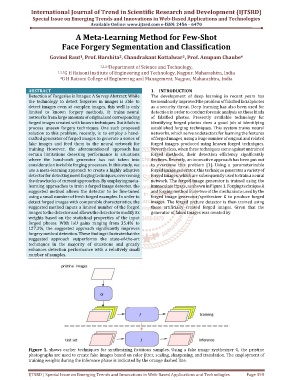
Figure 1. shows earlier techniques for synthesizing fictitious samples. Using a fake image synthesizer G, the pristine
photographs are used to create fake images based on color jitter, scaling, sharpening, and translation. The employment of
training weights during the inference phase is indicated by the orange dashed line.
IJTSRD | Special Issue on Emerging Trends and Innovations in Web-Based Applications and Technologies Page 398