Page 412 - Emerging Trends and Innovations in Web-Based Applications and Technologies
P. 412
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) @ www.ijtsrd.com eISSN: 2456-6470
Face2Face, and NeuralTextures are fake, while MT_Old is the
best at detecting the unseen method FaceSwap.
5. Conclusion
Instead of developing a false picture detector with a big
training dataset encompassing a variety of forgery
techniques, this study used meta-learning to train a neural
network capable of recognizing phony photos produced by
multiple undetectable forgery strategies with a small number
of samples. The suggested technique emphasizes the usage of
data from a small number of samples in order to rapidly
update the false detector. Despite the limited sample size, the
experimental findings suggest that the proposed approach
can greatly increase performance metrics such as AUC,
accuracy, and IoU. This demonstrates that this strategy is
worth examining further. Improving feature extraction from
a small number of samples and broadening the range of
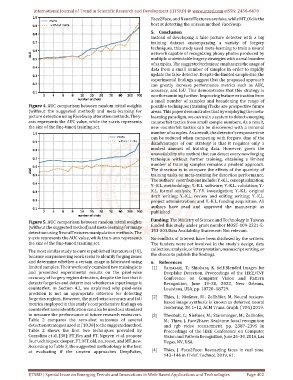
Figure 4. AUC comparison between random initial weights possible techniques (training)Tasks are prospective future
(without the suggested method) and meta-learning for areas. This paper demonstrates that by employing the meta-
picture detection using FaceSwap alteration methods. The y- learning paradigm, we can train a system to detect emerging
axis represents the AUC value, while the x-axis represents counterfeit tactics from small sample numbers. As a result,
the size of the fine-tuned training set. new counterfeit tactics can be discovered with a minimal
number of samples. As a result, the detector's response time
can be reduced when competing with forgers. One of the
disadvantages of our strategy is that it requires only a
modest amount of training data. However, given the
unavailability of a method that can detect every new forging
technique without further training, obtaining a limited
number of training samples remains a prudent approach.
The direction is to compare the effects of the quantity of
training tasks on meta-training for detection performance.
The authors' contributions include: Y.-K.L. conceptualization;
Y.-K.L. methodology; Y.-K.L. software; Y.-K.L. validation; Y.-
K.L. formal analysis; T.-Y.Y. investigation; Y.-K.L. original
draft writing; Y.-K.L. review and editing writing; Y.-K.L.
project administration; and Y.-K.L. funding acquisition. All
authors have read and approved the manuscript as
published.
Funding: The Ministry of Science and Technology in Taiwan
Figure 5. AUC comparison between random initial weights
(without the suggested method) and meta-learning for image funded this study under grant number MOST-109-2221-E-
detection using NeuralTextures manipulation methods. The 153-003.Data Availability Statement: Not relevant.
y-axis represents the AUC value, while the x-axis represents No conflicts of interest have been disclosed by the writers.
the size of the fine-tuned training set. The funders were not involved in the study's design, data
collection, analysis, or interpretation, manuscript writing, or
The most similar study to ours in published literature is [10],
the choice to publish the findings.
because our pioneering work seeks to identify forging zones
and determine whether a certain image is fabricated using 6. References
limited samples. Their work only examined two training sets [1] Yamasaki, T.; Shiohara, K. Self-Blended Images for
and presented experimental results on the pixel-wise Deepfake Detection. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF
accuracy of forgery region detection, despite the fact that it Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
detects forgeries and determines whether an input image is Recognition, June 19–20, 2022, New Orleans,
counterfeit. In Section 4.2, we explained why pixel-wise Louisiana, USA, pp. 18720–18729.
precision is not an appropriate criterion for detecting [2]
forgeries regions. However, the pixel-wise accuracy and IoU Thies, J.; Nießner, M.; Zollhöfer, M. Neural texture-
metrics employed in this study's comprehensive findings on based image synthesis is known as deferred neural
counterfeit zone identification can also be used as a standard rendering. 38, 1–12, ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2019.
to measure the performance of future research endeavors. [3] Theobalt, C.; Nießner, M.; Stamminger, M.; Zollhofer,
Table 2 compares the zero-shot outcomes of several M.; Thies, J. Face2Face: Real-time facial recognition
detection strategies used in [10,38] to the suggested method. and rgb video reenactment. pp. 2387–2395 in
Table 2 shows the first two techniques provided by Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer
Cozzolino et al. [38]: FT_Res and FT. Nguyen et al. propose Vision and Pattern Recognition, June 26–30, 2016, Las
four techniques: deeper_FT, MT_old, no_recon, and MT_new. Vegas, NV, USA.
According to Table 2, the suggested methodology is the best [4]
at evaluating if the unseen approaches DeepFakes, Thies, J. Face2Face: Reenacting faces in real time.
143–146 in IT-Inf. Technol. 2019, 61.
IJTSRD | Special Issue on Emerging Trends and Innovations in Web-Based Applications and Technologies Page 402