Page 410 - Emerging Trends and Innovations in Web-Based Applications and Technologies
P. 410
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) @ www.ijtsrd.com eISSN: 2456-6470
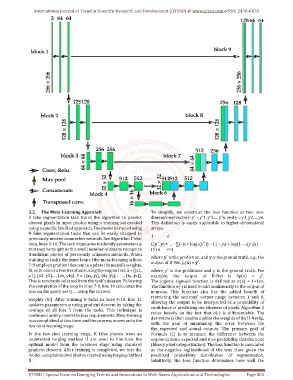
3.2. The Meta-Learning Approach To simplify, we construct the loss function as two one-
A fake segmentation task trains the algorithm to predict dimensional vectors: yˆ = yˆ1, yˆ2,..., yˆn, and y = y1, y2,..., yn.
altered pixels in input photos using a training set created This definition is easily applicable to higher-dimensional
using a specific falsified approach. The model is trained using arrays.
N fake segmentation tasks that can be easily changed to
1 n
previously unseen counterfeit methods. See Algorithm 1's for
loop, lines 3-10. The technique aims to identify parameters φ L(yˆ, y) = · ∑(−yi × log(σ(yˆi)) − (1 − yi) × log(1 − σ(yˆi)))
that may be taught with a small number of data to recognize (1) n i=1
fraudulent photos of previously unknown methods. When
where yˆ is the prediction, and y is the ground truth, e.g., the
training on task i, the inner loop of the meta-learning in lines
output of U-Net fφ(x) = yˆ.
7-9 employs gradient descent to update the model's weights,
θi, with one or a few iterations using the support set, S = {(x1, where yˆ is the prediction and y is the ground truth. For
y1), (x2, y2),..., (xk, yk)}. S = {(x1, y1), (x2, y2), . . . , (xk, yk)}, example, the output of U-Net is fφ(x) = yˆ.
This is randomly selected from the task's dataset. Following The logistic sigmoid function is defined as σ(x) = 1+1ex.
the completion of the loop in lines 7-9, line 10 calculates the The function σ(·) is used to add nonlinearity to the output of
loss on the query set Q,..., using the current neurons. This function also has the added benefit of
restricting the neurons' output range between 1 and 0,
weights (θi). After training N tasks in lines 4-10, line 11
allowing the output to be interpreted as a probability of
updates parameters φ using gradient descent by taking the
confidence in predicting the fakeness of pixels. Algorithm 1
average of all loss 'i from the tasks. This technique is
relies heavily on the fact that σ(·) is differentiable. The
continued until φ meets the loss requirements. Meta-training
derivative is then used to update the weights of the U-Net fφ,
is accomplished at this time, and the process moves on to the
with the goal of minimizing the error between the
few-shot learning stage.
the expected and actual outputs. The primary goal of
In the few-shot learning stage, K false photos from an Formula (1) is to measure the difference between the
undetected forging method U are used to fine-tune the segmentation's expected and true probability distributions
optimal model from the previous stage using standard (binary pixel categorization). The loss function is calculated
gradient descent. After training is completed, we test the as the negative loglikelihood of the true class given the
model using fabricated photos created using forging method predicted probability distribution of segmentation.
U. Intuitively, the loss function determines how well the
IJTSRD | Special Issue on Emerging Trends and Innovations in Web-Based Applications and Technologies Page 400