Page 601 - Emerging Trends and Innovations in Web-Based Applications and Technologies
P. 601
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) @ www.ijtsrd.com eISSN: 2456-6470
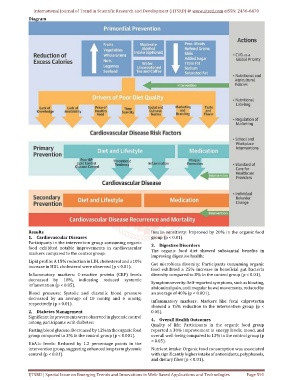
Diagram
Results Insulin sensitivity: Improved by 20% in the organic food
1. Cardiovascular Diseases group (p < 0.01).
Participants in the intervention group consuming organic 3. Digestive Disorders
food exhibited notable improvements in cardiovascular The organic food diet showed substantial benefits in
markers compared to the control group:
improving digestive health:
Lipid profile: A 15% reduction in LDL cholesterol and a 10% Gut microbiota diversity: Participants consuming organic
increase in HDL cholesterol were observed (p < 0.01).
food exhibited a 25% increase in beneficial gut bacteria
Inflammatory markers: C-reactive protein (CRP) levels diversity compared to 8% in the control group (p < 0.01).
decreased by 18%, indicating reduced systemic
Symptom severity: Self-reported symptoms, such as bloating,
inflammation (p < 0.05).
abdominal pain, and irregular bowel movements, reduced by
Blood pressure: Systolic and diastolic blood pressure an average of 40% (p < 0.001).
decreased by an average of 10 mmHg and 6 mmHg,
Inflammatory markers: Markers like fecal calprotectin
respectively (p < 0.01).
showed a 15% reduction in the intervention group (p <
2. Diabetes Management 0.05).
Significant improvements were observed in glycemic control 4. Overall Health Outcomes
among participants with diabetes:
Quality of life: Participants in the organic food group
Fasting blood glucose: Decreased by 12% in the organic food reported a 30% improvement in energy levels, mood, and
group compared to 3% in the control group (p < 0.001). overall well-being compared to 12% in the control group (p
< 0.05).
HbA1c levels: Reduced by 1.2 percentage points in the
intervention group, suggesting enhanced long-term glycemic Nutrient intake: Organic food consumption was associated
control (p < 0.01). with significantly higher intake of antioxidants, polyphenols,
and dietary fiber (p < 0.01).
IJTSRD | Special Issue on Emerging Trends and Innovations in Web-Based Applications and Technologies Page 591