Page 437 - Emerging Trends and Innovations in Web-Based Applications and Technologies
P. 437
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) @ www.ijtsrd.com eISSN: 2456-6470
B. Problem Statement
Despite the growing adoption of advanced cybersecurity technologies, many critical infrastructure systems remain vulnerable
to cyberattacks. The lack of real-time threat monitoring capabilities, insufficient information sharing, and delayed incident
responses exacerbate these vulnerabilities. InfraGuard has emerged as a promising mechanism to address these issues, but its
full potential in securing critical infrastructure against evolving cyber threats needs further exploration.
II. RELATED WORK
A. Evolution of Cyber Threats to Critical Infrastructure
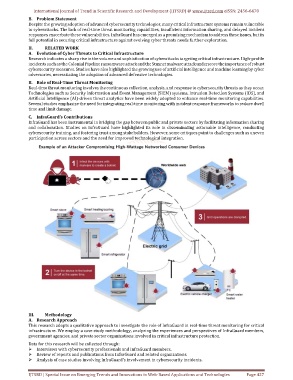
Research indicates a sharp rise in the volume and sophistication of cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure. High-profile
incidents such as the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack and the Stuxnet malware attack underscore the importance of robust
cybersecurity measures. Studies have also highlighted the growing use of artificial intelligence and machine learning by cyber
adversaries, necessitating the adoption of advanced defensive technologies.
B. Role of Real-Time Threat Monitoring
Real-time threat monitoring involves the continuous collection, analysis, and response to cybersecurity threats as they occur.
Technologies such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), and
Artificial Intelligence (AI)-driven threat analytics have been widely adopted to enhance real-time monitoring capabilities.
Several studies emphasize the need for integrating real-time monitoring with incident response frameworks to reduce dwell
time and limit damage.
C. InfraGuard’s Contributions
InfraGuard has been instrumental in bridging the gap between public and private sectors by facilitating information sharing
and collaboration. Studies on InfraGuard have highlighted its role in disseminating actionable intelligence, conducting
cybersecurity training, and fostering trust among stakeholders. However, some critiques point to challenges such as uneven
participation across sectors and the need for improved technological integration.
III. Methodology
A. Research Approach
This research adopts a qualitative approach to investigate the role of InfraGuard in real-time threat monitoring for critical
infrastructure. We employ a case study methodology, analyzing the experiences and perspectives of InfraGuard members,
government agencies, and private sector organizations involved in critical infrastructure protection.
Data for this research will be collected through:
Interviews with cybersecurity professionals and InfraGuard members.
Review of reports and publications from InfraGuard and related organizations.
Analysis of case studies involving InfraGuard's involvement in cybersecurity incidents.
IJTSRD | Special Issue on Emerging Trends and Innovations in Web-Based Applications and Technologies Page 427