Page 30 - Special Issue Modern Trends in Scientific Research and Development, Case of Asia
P. 30
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) @ www.ijtsrd.com eISSN: 2456-6470
objectives are not set, then the content and didactic structure require a higher level of mastery of the learning material
of the lesson is violated. It is important to develop pre- than comprehension.
appropriate learning objectives for the formation of
theoretical and practical lessons. 4. Analysis - the ability to divide the whole into elements,
the gradation of these elements and the ability to
establish relationships, to know the principles of
Results and Discussions
organization of the whole. In this case, the learning
By classifying learning objectives into categories and
sequential levels, it is recommended that pedagogical outcomes are characterized by their high intellectual
level in terms of understanding and application, as it
taxonomies be used to clearly articulate learning objectives.
requires knowledge of the content of the learning
Taxonomy (derived from the Greek word and "taxis" - to
place in order and "homos" - to mean law). Taxonomy material and its internal structure.
includes a category that is structured based on the natural 5. Synthesis - the creation of a whole of given elements in
relationship of objects and is based on a multi-step principle order to create new structures. Appropriate results
for describing objects. American educator B. Blum's represent a creative activity aimed at creating new
taxonomy of learning objectives is the most common schemes and structures.
taxonomy in the world. In practice, learning objectives are
6. Evaluation - the evaluation of materials and methods
developed for each theoretical and practical lesson. These
taking into account the adopted objectives. This category
goals are categorized in the taxonomy from the following
perspective: requires the achievement of learning outcomes based on
all previous categories and evaluative opinions based on
1. To know is to remember and recall facts and principles. clearly distinguishable criteria.
In this case, the listener can remember the acquired
knowledge and tell it. Adequate verbs are used to define learning objectives, ie the
purpose of the subject should be defined in such a way that
2. Understanding - is an indicator of the ability to
the purpose is clear, so the basic phrases on each topic
understand the essence of the studied material, draw
conclusions, analyze the current situation. Interpreting should be specified separately. It will be necessary to set the
depth of each basic phrase, the study. That is, the listener will
as an indicator of understanding, summarizing the
have to master one basic phrase at the level of knowledge,
material, or making suggestions about subsequent
the other at the level of evaluation of some basic phrases. An
events, and so on.
example of the coordination of verbs in the clear
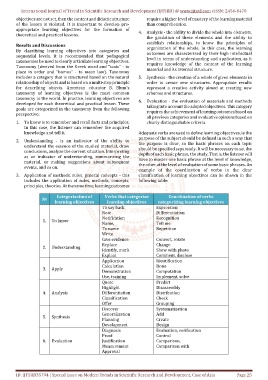
3. Application of methods, rules, general concepts - this classification of learning objectives can be shown in the
includes the application of rules, methods, concepts, following table:
principles, theories. At the same time, learning outcomes
Categorization of Verbs that categorize Coordination of verbs
№
learning objectives learning objectives categorizing learning objectives
To say back Expression
Note Differentiation
Notification Recognition
1. To know
Name, Tell me
To name Repetition
Write
Give evidence Convert, rotate
Replace Change
2. Understanding
Identify, mark Show with photo
Explain Comment, disclose
Application Identification
Calculation Done
3. Apply
Demonstration Computation
Use, training Implement, solve
Quote Predict
Highlight Disassembly
4. Analysis Differentiation Distribution
Classification Check
Offer Grouping
Discover Systematization
Generalization Add
5. Synthesis
Planning Create
Development Design
Diagnosis Evaluation, verification
Proof Control
6. Evaluation Justification Comparison,
Measurement Comparison with
Approval
ID: IJTSRD35794 | Special Issue on Modern Trends in Scientific Research and Development, Case of Asia Page 25