Page 63 - Combine
P. 63
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) @ www.ijtsrd.com eISSN: 2456-6470
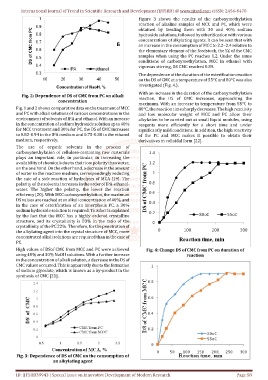
Figure 3 shows the results of the carboxymethylation
reaction of alkaline samples of MCC and PC, which were
obtained by treating them with 30 and 40% sodium
hydroxide solutions, followed by etherification with various
concentrations of alkylating agents. It can be seen that with
an increase in the consumption of MCC to 2.2–2.4 relative to
the elementary element of the feedstock, the SZ of the CMC
samples when using the PC reaches 1.2. Under the same
conditions of carboxymethylation, MCC in ethanol with
vigorous stirring, DS CMC reached 0.89.
The dependence of the duration of the esterification reaction
on the DS of CMC at a temperature of 55°C and 80°C was also
investigated (Fig. 4.).
With an increase in the duration of the carboxymethylation
Fig. 2: Dependence of DS of CMC from PC on alkali reaction, the DS of CMC increases, approaching the
concentration
maximum. With an increase in temperature from 55°C to
Fig. 1 and 2 shows comparative data on the treatment of MCC 80°C, the reaction time sharply decreases. The high reactivity
and PC with alkali solutions of various concentrations in the and low molecular weight of MCC and PC allow their
environment of solvents of IPA and ethanol. With an increase alkylation to be carried out at small liquid modules, using
in the concentration of sodium hydroxide solution up to 40% reagents more efficiently for a short time and under
for MCC treatment and 30% for PC, the DS of CMC increases significantly mild conditions. In addition, the high reactivity
to 0.82-0.94 in the IPA medium and 0.75-0.88 in the ethanol of the PC and MCC makes it possible to obtain their
medium, respectively. derivatives in colloidal form [22].
The use of organic solvents in the process of
carboxymethylation of cellulose-containing raw materials
plays an important role, in particular, in increasing the
availability of chemicals due to their low polarity than water,
on the one hand. On the other hand, a decrease in the amount
of water in the reaction medium, correspondingly reducing
the rate of a side reaction of hydrolysis of MCA [19]. The
polarity of the solvents increases in the order of IPA-ethanol-
water. The higher the polarity, the lower the reaction
efficiency [20]. With MCC carboxymethylation, the maximum
DS values are reached at an alkali concentration of 40%, and
in the case of esterification of an amorphous PC, a 30%
sodium hydroxide solution is required. This fact is explained
by the fact that the MCC has a highly ordered crystalline
structure, and its crystallinity is 83% in the ratio of the
crystallinity of the PC 22%. Therefore, for the penetration of
the alkylating agent into the crystal structure of MCC, more
concentrated alkali solutions are required than in the case of
PC.
High values of DSof CMC from MCC and PC were achieved Fig. 4: Change DS of CMC from PC on duration of
using 40% and 30% NaOH solutions. With a further increase reaction
in the concentration of alkali solution, a decrease in the DS of
CMC values occurred. This is apparently due to the formation
of sodium glycolate, which is known as a by-product in the
synthesis of CMC [21].
Fig. 3: Dependence of DS of CMC on the consumption of
an alkylating agent
ID: IJTSRD39943 | Special Issue on Innovative Development of Modern Research Page 58