Page 93 - Combine
P. 93
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) @ www.ijtsrd.com eISSN: 2456-6470
Statistical processing of the results of the study was carried out using the program "STATISTICA 6.0". We used: the
Kolmogorov–Smirnov test to assess the statistical significance of the difference when comparing the indicator of two
independent groups; the Spearman test to conduct a correlation analysis. In all measurements, the arithmetic mean was used as
an indicator of the average value, and the standard deviation was used for the spread indicator.
Results and discussion
All 54 patients included in the study had manifestations of multiple organ failure: the SAPS II index ranged from 50 to 86 (an
average of 74.4±11.2). 30 patients died. The level of cardiac troponin-T was in the range of 0.06-2.0 ng/ml (on average,
1.21±0.12).
In 22 patients out of 54 (40.7%), the final diagnosis was MINE. The diagnosis of AMI was made on the basis of the appearance
of the characteristic dynamics of the ECG, the progression of congestive left ventricular failure. In 7 patients, AMI occurred on
the background of decompensated diabetes mellitus, in 9 patients, AMI was repeated, and in 7 patients, there was repeated AMI
on the background of decompensated diabetes mellitus. Of the 22 patients with AMI, 11 patients died, and the diagnosis of AMI
was confirmed by autopsy.
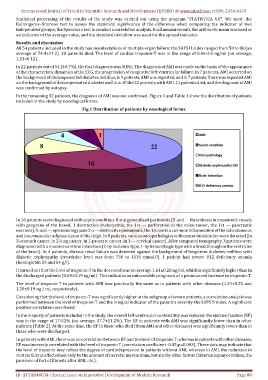
In the remaining 32 patients, the diagnosis of AMI was not confirmed. Figure 1 and Table 1 show the distribution of patients
included in the study by nosological forms.
Fig.1 Distribution of patients by nosological forms
4 3 1 AMI
8 22 Septic condition
Oncopathology
16 Diabetic nephropathy CRF
Brain infarction
B12-deficiency anemia
In 16 patients were diagnosed with septic condition: 8 and generalized peritonitis (5-and — thrombosis in mesenteric vessels
with gangrene of the bowel, 1 destructive cholecystitis, the 1st — perforation of the colon tumor, the 1st — pancreatic
necrosis), 5-and — epistemology jade 2-x —destructive pneumonia, the 1st one is a common inflammation of the subcutaneous
and intermuscular adipose tissue of the thigh. In 8 patients, various oncopathologies with cancer intoxication were detected (in
3-stomach cancer, in 2-lung cancer, in 1-prostate cancer, in 1 — cervical cancer). After computed tomography, 3 patients were
diagnosed with a massive cerebral infarction (2-by ischemic type, 1-by hemorrhagic type with a breakthrough in the ventricles
of the brain). In 4 patients, chronic renal failure was detected against the background of long-term diabetes mellitus with
diabetic nephropathy (creatinine level was from 730 to 1131 mmol/l). 1 patient had severe B12 deficiency anemia
(hemoglobin 59 and 64 g/l).
It turned out that the level of troponin-T in the deceased was on average 1.61±0.28 ng/ml, which is significantly higher than in
the discharged patients (0.64±0.19 ng/ml). This indicates an unfavorable prognosis of a pronounced increase in troponin-T.
The level of troponin-T in patients with AMI was practically the same as in patients with other diseases (1.24±0.21 and
1.20±0.19 ng / ml, respectively).
Considering that the level of troponin-T was significantly higher in the subgroup of severe patients, a correlation analysis was
performed between the level of troponin-T and the integral indicator of the patient's severity-the SAPS II index. A significant
positive correlation was found.
In the majority of patients included in the study, the overall left ventricular contractility was reduced: the ejection fraction (EF)
was in the range of 17-52% (on average, 37.7±11.2%). The EF in patients with AMI was significantly lower than in other
patients (Table 2). At the same time, the EF in those who died (from AMI and other diseases) was significantly lower than in
those who were discharged.
In patients with AMI, there was no correlation between EF and the level of troponin-T, whereas in patients with other diseases,
EF was inversely correlated with the level of troponin T (correlation coefficient -0.45;p=0.003). These data may indicate that
the level of troponin may reflect the degree of cardiodepression in patients without AMI, whereas in AMI, the reduction in
contractility is affected not only by the amount of necrotic myocardium, but also by other factors (hibernating myocardium, the
presence of foci of fibrosis after AMI, etc.).
ID: IJTSRD40034 | Special Issue on Innovative Development of Modern Research Page 88